China has emerged as a significant player in the global oil trading landscape in recent years, reshaping the dynamics of oil markets and garnering attention worldwide. Its rise can be attributed to factors such as its growing energy consumption, strategic partnerships with oil-producing nations, and vertical integration in the refining sector. China’s increased presence in the oil market has diversified trading patterns, influenced global oil prices, and impacted diplomatic relations and geopolitical strategies. Furthermore, its role has fostered economic interdependence with oil-producing countries, contributing to global trade, investment, and economic development. If you are interested in Oil trading investment, you may consider using oilprofit.app, a reputable trading platform online.
China’s Increasing Demand for Oil
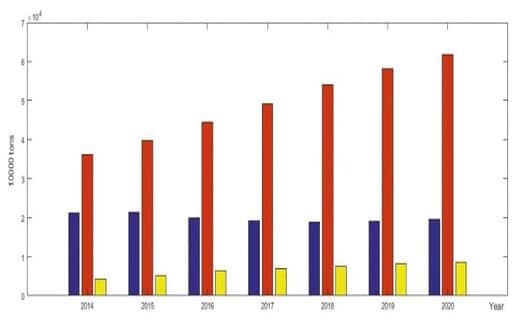
China, being the world’s largest energy consumer, has experienced rapid industrialization and urbanization in the past few decades. This has led to a surge in its energy requirements, particularly for oil. As the country’s population continues to grow and living standards improve, the demand for energy, including oil, is expected to escalate further.
Strategic Investments in Oil Infrastructure
To meet its escalating oil demands, China has strategically invested in oil infrastructure projects both domestically and internationally. The country has developed vast storage facilities, refineries, and pipeline networks to ensure a steady supply of crude oil. Additionally, China has made substantial investments in oil-producing regions, securing access to key reserves and forming long-term partnerships with major oil-producing nations.
Belt and Road Initiative
China’s Belt and Road Initiative, a massive infrastructure and economic development project, has further bolstered its influence in the global oil trading landscape. The BRI aims to connect China with over 70 countries across Asia, Europe, and Africa through a network of roads, railways, ports, and pipelines. By improving connectivity and trade routes, China enhances its access to oil-producing regions and establishes vital energy corridors.
Expanding Trade Partnerships
China has actively pursued trade partnerships with major oil-producing countries, reducing its reliance on traditional suppliers. It has formed strategic alliances with nations such as Russia, Saudi Arabia, Iran, and Angola, among others, to secure a diverse and stable supply of oil. By diversifying its sources, China mitigates potential risks associated with geopolitical tensions or supply disruptions in any particular region.
Growing Influence in Oil Pricing
Traditionally, oil prices were primarily determined by the Western-dominated futures markets. However, China’s increasing prominence in the global oil trading landscape has shifted this dynamic. As the world’s largest crude oil importer, China has started to exert its influence on oil pricing by introducing the Shanghai International Energy Exchange The ONE allows oil contracts to be traded in Chinese currency, the yuan, challenging the dominance of the US dollar in global oil transactions.
The Role of State-Owned Enterprises
China’s state-owned enterprises play a crucial role in its oil trading activities. Companies like China National Petroleum Corporation Sinopec, and CNOOC dominate the country’s oil industry and have expanded their operations globally. These SOEs possess significant financial resources and government backing, enabling them to secure favorable deals, invest in exploration and production, and control key parts of the oil supply chain.
Environmental Concerns and Transition to Cleaner Energy
As global concerns over climate change and environmental sustainability mount, China has been actively transitioning to cleaner energy sources. While it remains a major consumer of oil, the country has also made significant investments in renewable energy, electric vehicles, and alternative fuels. This transition aligns with China’s broader goals of reducing pollution and achieving carbon neutrality, thereby impacting its long-term oil trading strategies.
Geopolitical Implications
China’s growing influence in the global oil trading landscape has significant geopolitical implications. It strengthens the country’s position as a major global player and grants it leverage in diplomatic negotiations. By securing energy resources and trade partnerships, China enhances its economic and political ties with oil-producing nations, influencing regional dynamics and potentially challenging the existing geopolitical balance.
Conclusion
In conclusion,China’s rise in the global oil trading landscape is a testament to its growing economic prowess and strategic vision. The country’s increasing demand for oil, coupled with its investments in infrastructure, trade partnerships, and pricing mechanisms, have reshaped the dynamics of global oil markets. As China continues to expand its influence in the energy sector, the ramifications will extend far beyond oil trading, impacting geopolitics, environmental policies, and the overall global economy.