How to use Switch Case statement in Java?
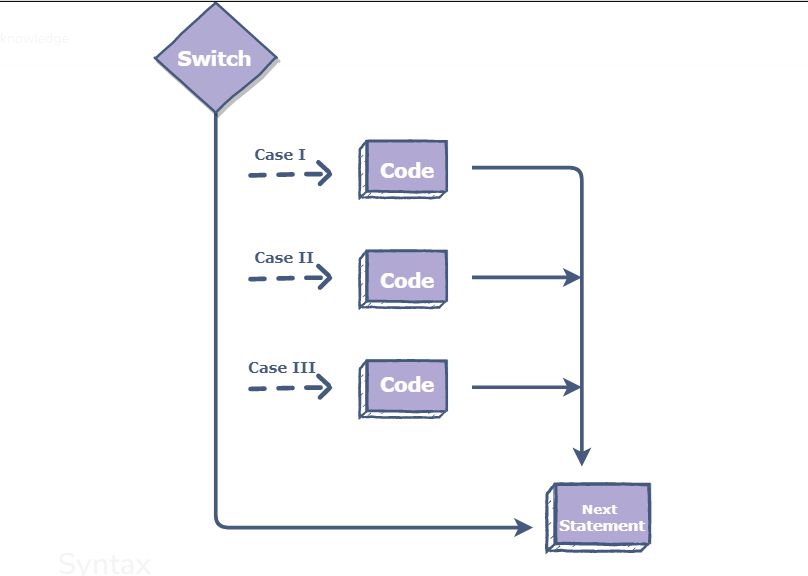
In Java, a switch statement is used to transfer control to a particular block of code, based on the value of the variable being tested.
Note: Switch statements are an efficient alternative for if-else statements.
How it works
The switch is passed a variable, the value of which is compared with each case value. If there is a match, the corresponding block of code is executed.
Syntax :
The Any Programming language general primary syntax of the switch statement like as a Java, PHP, C++ or any other is as bellows:
switch (variable)
{
case value_1:
//code
case value_2:
//code
default:
//code
}
The simple Java variable passed to the switch can be of following the all Data types:
- Integer
- Strings
- Enums
Also You can Read my prev Article like as a java string to char array
switch statement java example
Example : what is a switch statement in java?
Consider the following example to get a better idea of how the switch statement works.
If you want to write a piece of code which prints the upcomming forecast corresponding to the given input.
class HelloWorld {
public static void main( String args[] ) {
int upcomming = 2;
//passing variable to the switch
switch (upcomming)
{
//comparing value of variable against each case
case 0:
System.out.println("It is Hollywood today!");
break;
case 1:
System.out.println("It is Bollywood today!");
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("It is Tamil today!");
break;
//optional
default:
System.out.println("Sorry Dear, Invalid Input!");
}
}
}
Note:
- Duplicate case values are not allowed.
- The value of a case must be the same data type as the variable in the switch.
- Adding the default case is optional but handling unexpected input is considered a good programming practice.
If the simply use a break statement is not used, all main available cases after the right case are successfully executed.
Run the following bellow Source code to see what happens if we eliminate the break statement from each code block: restart switch statement java
class HelloWorld {
public static void main( String args[] ) {
int upcomming = 0;
//here simple the passing variable to the switch conditions
switch (upcomming)
{
//comparing some data value of variable against each case
case 0:
System.out.println("It is Hollywood today!");
case 1:
System.out.println("It is Bollywood today!");
case 2:
System.out.println("It is Tamil today!");
//some optional
default:
System.out.println("Sorry Dear, Invalid Input!");
}
}
}